GenomeSignature: Homologous Recombination Deficiency (HRD) Score assay
A predictive biomarker to targeted therapy with PARP inhibitors.

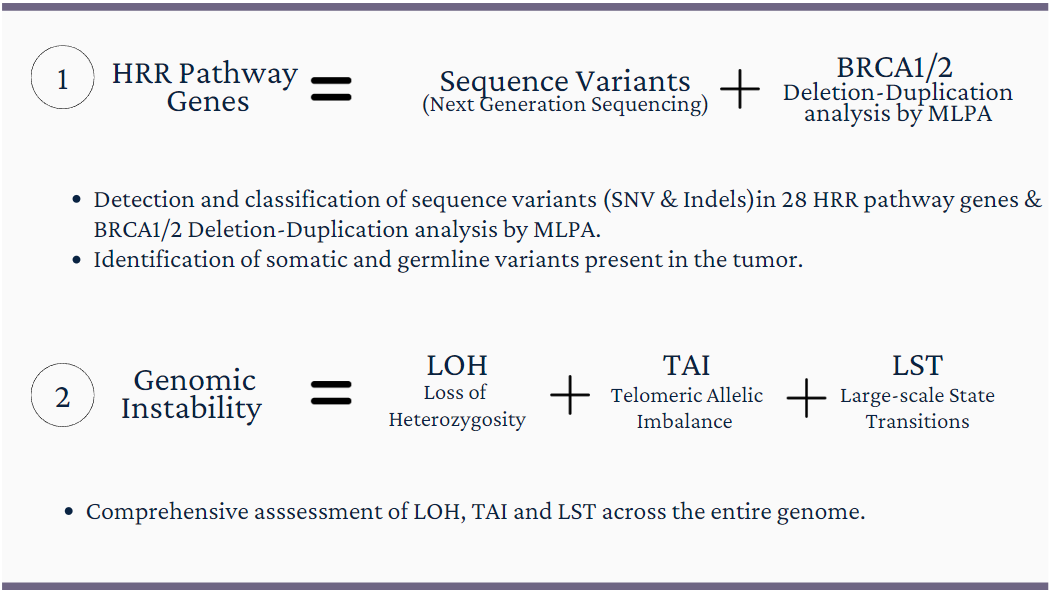
Assessment of Genomic Instability using three biomarkers: Loss of Heterozygosity (LOH), Telomeric Allelic Imbalance(NtAI) & Large-scale State Transitions (LST).
Get GenomeSignature Assay Brochure
Request Brochure on Your Whatsapp

Get GenomeSignature assay dummy report

Get GenomeSignature Dummy report on your WhatsApp
Tumors manifesting HRD are especially sensitive to PARP inhibitors, as these agents increase the number of double stranded breaks, making cell death more likely in cells also manifesting HRD. Therefore, HRD and the presence of HRR gene mutations have become biomarkers for assessing PARP inhibitor sensitivity.”
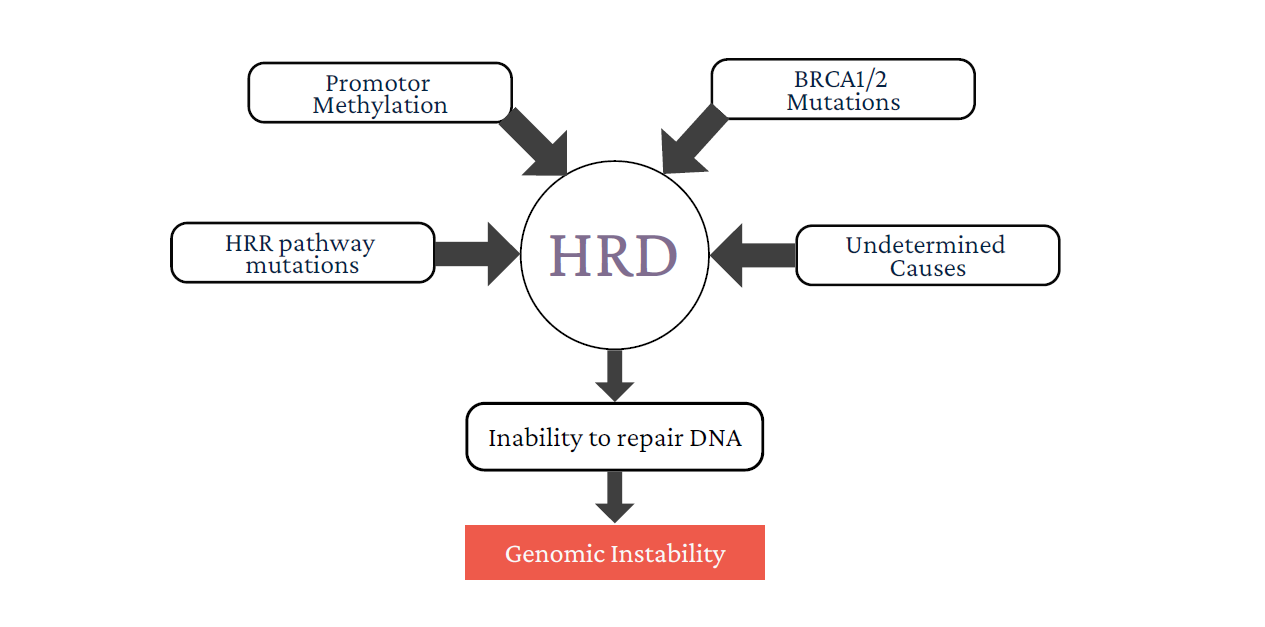
Homologous Recombination Deficiency is calculated by proprietary algorithm developed at Rophevac Bio Labz based on three biomarkers (loss of heterozygosity, telomeric allelic imbalance and large-scale state transitions).
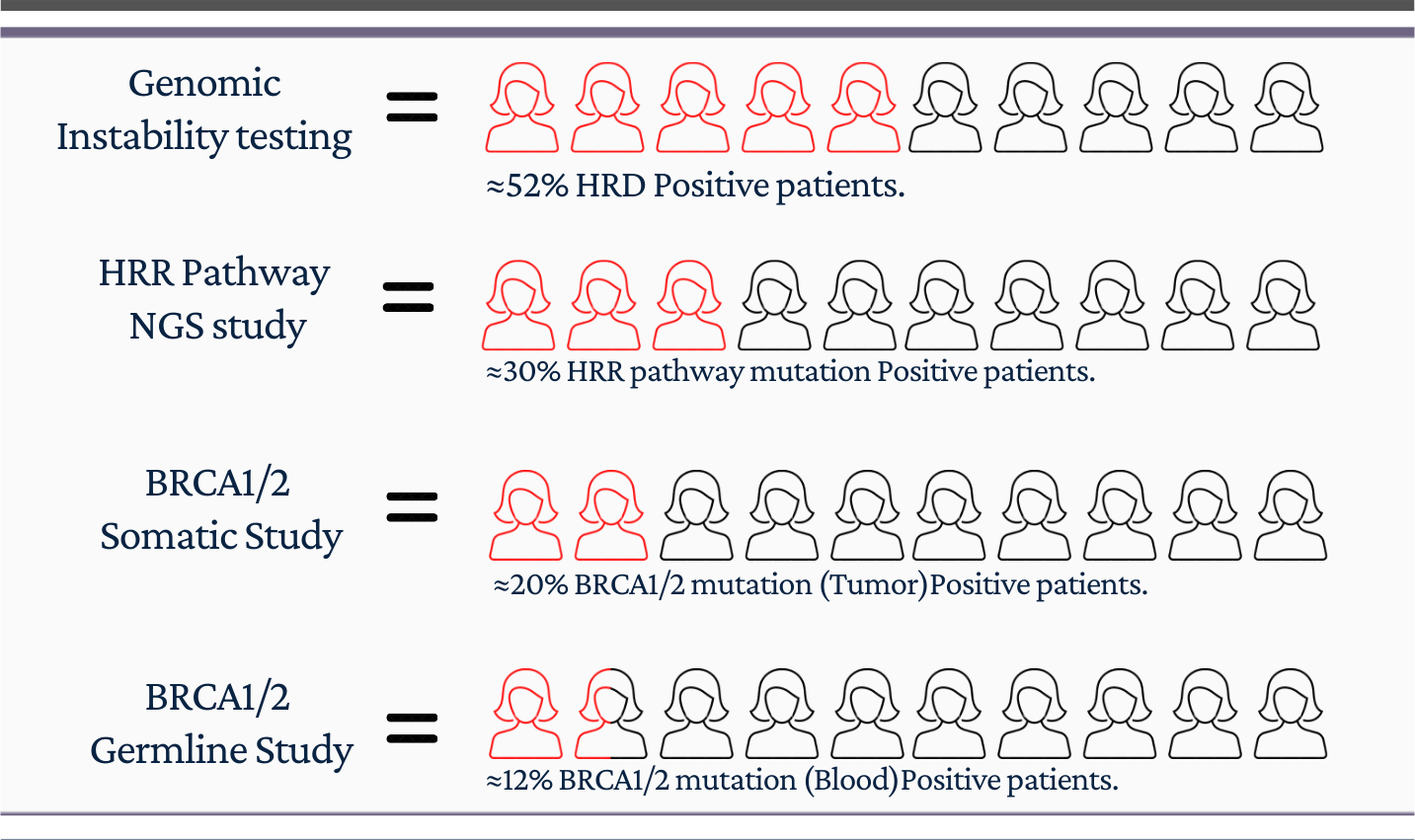
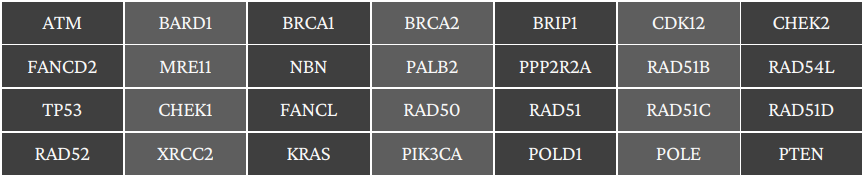
GenomeSignature assay Includes Somatic and Germline analysis for the presence of specific mutations within BRCA1, BRCA2 along with HRR pathway genes, (Total 28 genes) at high depth using Next Generation Sequencing.
GenomeSignature assay Includes BRCA1 and BRCA2 Germline study to analyse deletion/duplications. intended to confirm a potential cause for and clinical diagnosis of hereditary breast and ovarian cancer (HBOC) syndrome.
Most Causes of HRD are Unknown
Ovarian and breast tumors with loss of either BRCA1 or BRCA2 are particularly sensitive to treatment with platinum-based DNA crosslinking agents.
Some tumors with no apparent loss of BRCA1 or BRCA2 exhibit similar patterns of genomic scars, and also show increased sensitivity to treatment with platinum drugs. This suggests that defects in DNA repair other than BRCA1 or BRCA2 loss may also confer drug sensitivities similar to BRCA1/2 loss.
HRD describes a tumor that has an impaired ability to repair DNA double strand breaks through homologous recombination repair.
The GenomeSignature assay is designed to identify a comprehensive signature for Homologous Recombination Deficiency (HRD) by testing genome-wide single nucleotide variants in DNA extracted from FFPE tumor specimens.
Clinical and Therapeutic significance of HRD
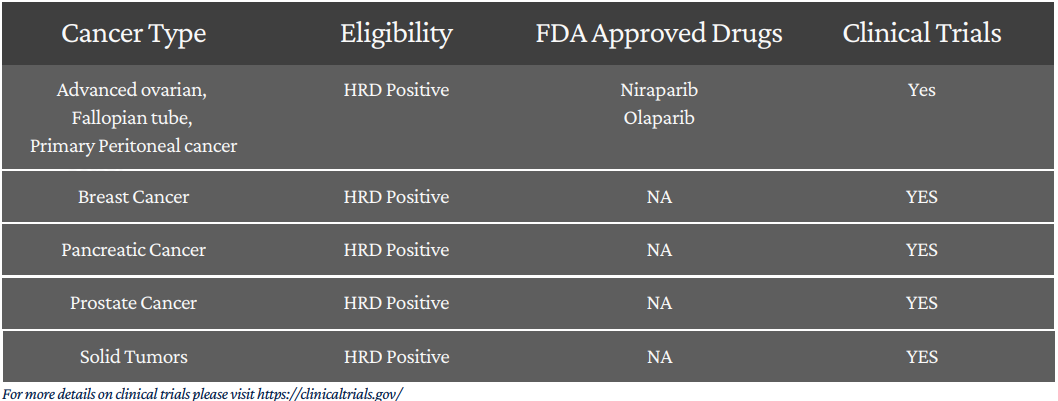
Identify more potentially eligible patients sensitive to PARP inhibitors
Positive patients by Testing Modality
HRR pathway genes covered in Panel
Germline + Somatic Study
State of the art Bioinformatics pipelines
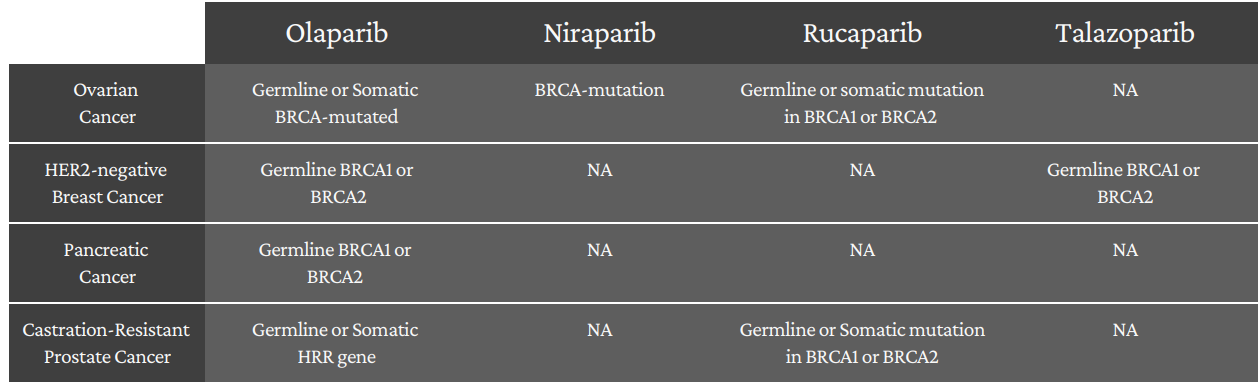
FDA Approved PARP Inhibitors
Rophevac Bio Labz
NABL accredited, dedicated genomics facility for Oncology, Rare Diseases & Reproductive health.